Italian National Agency for New Technologies, Energy and Sustainable Economic Development
Energy: Air conditioning, ENEA tips for sustainability and bill saving
As every year, ENEA shares eco-friendly, energy saving summer tips.
Here’s ENEA advice to keep your home cool and your utility bills in check while minimizing your environmental impact: in addition to how to improve the performance of existing air conditioners, ENEA experts recommend replacing older air conditioning units with a single heat pump system for both summer cooling and winter heating, which reduces both costs and environmental impact.
"In Italy there are currently more than 19 million gas boilers installed, between stand-alone and centralized systems, at least 7 million of which are more than 15 years old. So there is a huge potential for efficiency gains, considering also the approximately 1.7 million mono- and multi-split air conditioners installed before 2013, considerably less efficient than modern ones and nearing their life-span”, explained Nicolandrea Calabrese, head of the ENEA Energy Efficiency in Buildings and Urban Development Laboratory. "This intervention enables a typical family living in an apartment of about 70 m² to reduce both summer and winter air conditioning by 49 percent in Naples, 47 percent in Rome and 46 percent in Milan[1]. Then, with tax deductions, you can fall back on replacing expenses in about 6½ years in cities like Naples and Rome and about 4½ years in Milan," he said.
Heat pumps have shown to be more economical in the long run and can simplify system management and maintenance by integrating both winter heating and summer cooling in a single system. This system is the best way to increase thermal comfort, as it ensures an even and more stable temperature.
To ensure a smooth intervention, it is important a qualified technician first carries out an energy diagnosis of the building and checks whether the diameter of the existing piping may be sufficient for replacing radiators with fan coils, checks for the presence of an electrical outlet near the radiator (the fan coil requires an electrical connection to operate) and checks whether it is possible to install a drain for the condensation generated by the fan coil during summer operation.
In addition, unlike gas boilers, which no longer qualify for incentives, heat pumps benefit from tax deductions like the Home Bonus and Ecobonus, with different deduction rates starting from a 50 percent deduction for main homes and 36 percent for second homes and other properties.
"The economic benefit of a heat pump system can be maximized when combined with photovoltaic systems and electrical storage systems, which can help transform the building into a Zero Emission Building (ZEmB), as required by the new European EPBD IV Directive. Zero Emission Buildings are highly energy-efficient buildings that meet their energy needs through renewable sources and do not produce greenhouse gas emissions related to fossil fuels", Calabrese concludes.
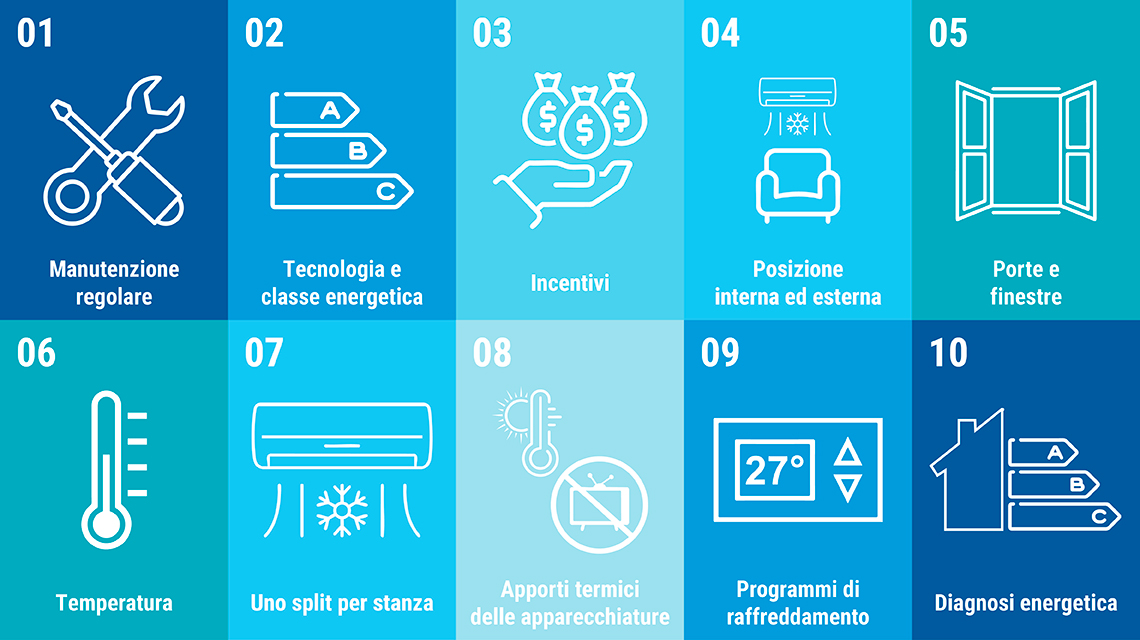
10 tips to make air conditioners more efficient
ENEA suggests ten simple actions to save on air conditioning, maximize comfort and benefit the environment
-
Regular maintenance
To ensure optimal performance, air conditioners require regular cleaning and maintenance, inspecting the refrigerant pipes which should be thermally insulated. Poorly maintained air conditioning systems consume up to 30% compared to factory parameters. In addition to the energy aspect, it is important to note that air filters and fans in unmaintained air conditioners more frequently harbor mold and bacteria that are harmful to health, including the potentially deadly legionella bacteria. The regulations require a system booklet and regular inspections for systems exceeding 12 kW for cooling and 10 kW for heating.
- Technology and energy class
A proper choice of an air conditioner is important to lower consumption and your energy bill. Regardless of the technology chosen, models with higher energy ratings (above A) generally translate to lower energy consumption and reduced CO2 emissions. For example, an appliance with an A+++ energy rating can consume up to 40% less electricity than an appliance with a B rating
Air conditioners with an inverter control system are a good choice when you plan to keep the air conditioning on for extended periods. Although more expensive than traditional on-off systems, they have lower energy consumption, reduced noise and provide greater comfort.
Significant economic benefits can be obtained by combining the system with a photovoltaic system. It is essential to synchronize the operation of the air conditioner with the peak energy production of the system, typically during midday
-
Incentives
|
Tax deduction |
Intervention |
|
Home bonus 50% |
Purchase of air conditioners made as part of building renovation or extraordinary maintenance work on main dwelling |
|
36% home bonus |
Purchase of air conditioners related to renovations or extraordinary maintenance on second homes |
|
Ecobonus 50% |
Purchase of high-efficiency heat pump air conditioners to replace a lower efficiency system in main home |
|
Ecobonus 36% |
Purchase of high-efficiency heat pump air conditioners to replace a lower efficiency system in second home |
For purchases incurred by December 31, 2025, the “air conditioner bonus” provides a 50% tax deduction
- Indoor and outdoor location
It is important to install the air conditioner high on the wall since cold air sinks and will mix more easily with warmer air, which rises instead. Avoid placing the air conditioner behind sofas or curtains because the barrier effect can prevent the cool air from circulating properly. It is also a good idea to make sure that the outdoor unit of the air conditioner is not exposed to direct sunlight and weather.
-
Doors and windows
Closing shutters, lowering blinds or shielding windows and doors with curtains during the hotter part of the day in summer reduces the amount of solar heat into the home and, consequently, the energy required by air conditioners.
The air conditioner cools and dehumidifies the room in which it is installed by transferring heat and humidity to the outside. When new warm air enters the room the air conditioner must work harder to bring the temperature and humidity back to the desired levels, resulting in an higher energy expenditure. Instead, it is advisable to open windows during the cooler nightime hours if the air conditioner is not running.
- Temperature
Regulations stipulate that during the summer season the indoor temperature should not drop below 26 degrees Celsius, but comfort is often achieved when the indoor temperature is a few degrees lower than the outdoor. Often the activation of the “dehumidification” function can alleviate the oppressive feeling of heat, because high humidity makes the perceived temperature higher than the actual temperature.
- One split per room
Installing a more "powerful" air conditioner in the corridor hoping that it will cool the entire house is useless: the only result will be to catch a cold every time you cross the corridor going from one room to another, as it will be the the only room to be cooled.
- Heat produced from appliances
During the hottest hours, it is advisable to limit the use of heat-producing appliances that contributes to increase indoor temperatures (computers, televisions, appliances, lights).
- Cooling programs
Set your thermostat to a comfortable temperature and set cooling programs to optimize energy consumption when you are away or at night.
These functions both increase comfort and reduce the amount of time the unit needs to run and minimize the time it takes to turn on the unit. They also allow you to remotely control your air conditioner keep it running just when needed. For example, the “night” or “sleep” function can adjust room temperature based on changes in body temperature during sleep.
- Energy Diagnosis
It is advisable to have a qualified technician carry out an energy diagnosis of the building to evaluate the thermal insulation of walls and windows and the efficiency of air conditioning systems. The diagnosis will suggest the most cost-effective interventions to be carried out. In addition to cutting costs for summer air conditioning of rooms even up to 40 percent, the interventions are even more cost-effective take advantage of tax deductions for building energy renovation.
